Understanding Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Introduction
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) is crucial for those grappling with this chronic skin condition. Often referred to simply as eczema, atopic dermatitis manifests as dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It affects millions globally, with its onset frequently occurring in childhood but persisting into adulthood for many.
Eczema's significance as a chronic ailment lies in its persistent nature and the discomfort it causes. Those affected often experience a cycle of flare-ups and remissions, impacting daily life quality. Recognizing the causes—such as genetic predispositions and immune system irregularities—alongside symptoms can empower individuals to manage their condition more effectively.
Key management strategies include:
- Identifying personal triggers
- Establishing a consistent skincare routine
- Seeking medical advice when necessary
These approaches not only alleviate symptoms but also improve overall well-being for those living with eczema. Understanding and addressing this condition can greatly enhance life quality.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Definition of Atopic Dermatitis
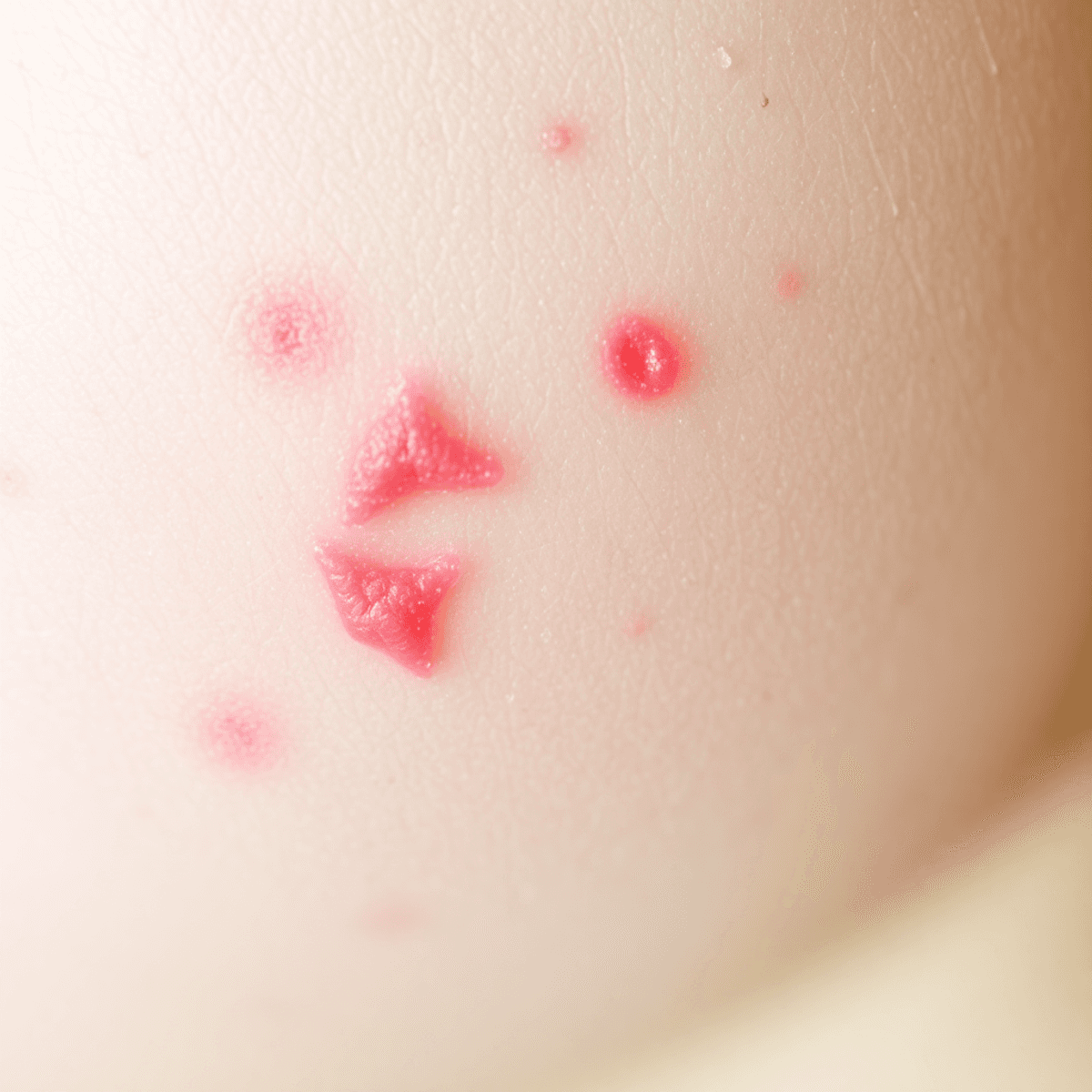
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a long-lasting inflammatory skin condition characterized by persistent dryness, itchiness, and inflammation. This condition often begins in childhood but can occur at any age. Eczema affects the skin's ability to retain moisture, resulting in weakened skin barriers.
Eczema Characteristics
Individuals with atopic dermatitis may experience:
- Dry Skin: The skin often appears rough and lacks moisture.
- Itchiness (Pruritus): A key symptom that can lead to scratching.
- Inflamed Skin: Redness and swelling are common features.
- Rashes: These can vary in appearance and severity, depending on factors like skin tone.
Understanding these characteristics is crucial for recognizing and managing the condition effectively.
Differentiating Eczema from Other Skin Conditions
Eczema shares similarities with other skin conditions such as psoriasis, contact dermatitis, and rosacea. However, it stands out due to its chronic nature and strong association with genetic predispositions and immune system variations. Unlike psoriasis, which typically presents with thicker scales, eczema primarily involves itch-driven inflammation. Recognizing these differences helps in accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Symptoms and Variability of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis has many symptoms, making it a complex skin condition to manage. The main signs include:
- Dry skin: The skin often feels rough and scaly, leading to discomfort.
- Itchy skin: This sensation can range from mild to intense, often resulting in persistent scratching.
- Inflamed skin: The itching can cause redness and warmth.
Rashes and Their Variability
Rashes are common in atopic dermatitis and may look different depending on the individual's skin tone. Here are some possible appearances of rashes:
- Small, raised bumps for some individuals
- Oozing and crusting when the skin becomes heavily irritated for others
Thickened or leathery patches can also occur due to chronic scratching or rubbing.
Understanding Individual Differences
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis can vary significantly from person to person. Each person's experience is unique; factors such as age, environmental triggers, and personal health conditions play a role. While one individual might struggle primarily with dryness and itching, another may face recurring bouts of inflamed skin and rash development.
Understanding this diversity in symptom presentation is crucial for effective management and treatment strategies tailored to each person's needs.
Causes and Risk Factors for Eczema Flare-ups
Understanding the causes of atopic dermatitis involves looking into genetic variations and immune response. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as individuals with a family history of eczema, hay fever, or asthma are more likely to develop the condition. Variations in the immune system's response can also contribute to flare-ups, with the skin's barrier function being compromised, leading to increased sensitivity and inflammation.
Key Factors Contributing to Eczema Flare-ups
- Genetics: Family history of eczema or related conditions increases risk.
- Immune Response: Variations in how the immune system reacts can trigger flare-ups.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: Compromised skin barrier leads to heightened sensitivity.
A notable aggravating factor is the presence of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. This bacterium can colonize the skin and worsen symptoms by disrupting its natural defenses. The overgrowth of Staphylococcus aureus often leads to more severe episodes of dryness, itchiness, and inflammation.
Common Risk Factors for Eczema Flare-ups
Certain risk factors heighten the likelihood of experiencing eczema flare-ups:
- Environmental factors: Exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander.
- Climate conditions: Cold, dry air or excessive heat can trigger symptoms.
- Personal factors: Stress and emotional distress may worsen eczema.
Recognizing these potential triggers is crucial for managing atopic dermatitis effectively. Identifying personal risk factors allows for tailored management strategies that aim to reduce flare-up frequency and severity.
Complications Associated with Atopic Dermatitis
Untreated or poorly managed atopic dermatitis can lead to several complications that affect both physical and mental well-being.
1. Neurodermatitis
Persistent scratching due to constant itching can result in neurodermatitis. This condition causes the skin to thicken, become discolored, and develop a leathery texture. The cycle of itching and scratching can exacerbate skin damage, making management even more challenging.
2. Mental Health Issues
There is a significant link between atopic dermatitis and mental health problems like anxiety and depression. The chronic nature of the condition, coupled with visible symptoms, often leads to self-consciousness and stress. Individuals may experience social withdrawal or disturbances in daily activities, amplifying feelings of anxiety or depression.
Addressing these complications requires an integrated approach focusing on both dermatological treatment and psychological support. Identifying early signs of neurodermatitis or mental health issues is crucial in minimizing long-term impacts.
Management Strategies for Eczema Control
1. Skincare Routine for Eczema Management
Developing an effective skincare routine is vital for managing and preventing eczema flares. A consistent approach helps maintain the skin's barrier function, reducing irritation and inflammation.
Moisturize Regularly
Keeping the skin hydrated is crucial in managing atopic dermatitis. Opt for rich, fragrance-free creams or ointments designed for sensitive skin. Products like Crema di Matteo or petroleum jelly can provide a protective layer, locking in moisture and soothing dry patches. Apply moisturizers immediately after bathing to seal in hydration.
Effective Bathing Practices
Bathing should be gentle and strategic to prevent flare-ups. Use lukewarm water instead of hot, as high temperatures can exacerbate dryness and itching. Limit baths or showers to 10-15 minutes to avoid stripping the skin of natural oils. Consider using mild, soap-free cleansers such as Il Bagno Body Wash, which boast formulations with up to 95% natural ingredients, minimizing irritation.
Pat Rather Than Rub
After bathing, gently pat your skin dry with a soft towel rather than rubbing it, which can irritate sensitive areas. This practice helps preserve the skin’s natural moisture.
Creating a customized skincare routine tailored to your specific needs is key to managing symptoms effectively. Different products work for different individuals, so experimenting with various options may be necessary to find what suits you best. Regularly moisturizing and adopting gentle bathing techniques are fundamental components of any eczema management plan.
By understanding atopic dermatitis and incorporating these daily practices into your routine, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups, improving your quality of life over time.
2. Identifying Triggers to Prevent Eczema Flare-ups
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) involves recognizing the importance of a proactive approach to managing this condition. Identifying and avoiding triggers is essential in minimizing flare-ups and maintaining healthy skin.
Common Triggers:
- Heat and Sweat: High temperatures can cause sweating, leading to skin irritation and worsening eczema symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate eczema, triggering flare-ups in many individuals.
- Dry Skin: A lack of moisture aggravates eczema, making regular moisturizing a critical prevention method for eczema flares.
- Allergens: Common allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and pollen are known irritants.
- Harsh Soaps and Detergents: These can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation.
Recognizing Individual Triggers:
Each person's experience with eczema is unique. It is crucial to monitor your skin's reaction to various environmental factors and lifestyle choices through careful observation. Keeping a diary to track symptoms against daily activities can help identify specific triggers.
By understanding these common triggers for eczema and recognizing individual sensitivities, you can take preventive measures that contribute significantly to managing atopic dermatitis effectively. Regularly moisturizing the skin and adapting living environments are simple yet effective strategies in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
Knowing when to consult about atopic dermatitis treatments is crucial in managing the condition effectively. Here are some signs that indicate you should seek professional medical advice:
- Persistent Itchiness: If the itching disrupts sleep or daily activities, it's time to seek help.
- Visible Skin Infections: New streaks, pus, or yellow scabs on the skin suggest an infection that requires medical attention.
- Unresponsive to Home Care: When over-the-counter treatments and home care routines fail to alleviate symptoms.
- Fever Accompaniment: A rash accompanied by fever signals an urgent need for medical evaluation.
- Severe Flare-ups: If flare-ups are frequent or severe, a healthcare provider can offer personalized treatment options.
Engaging with a healthcare professional ensures appropriate management strategies are in place, reducing the risk of complications and improving quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. While a cure remains elusive, self-care strategies combined with medical interventions offer a way to control symptoms and prevent complications. By adopting a consistent skincare routine, identifying triggers, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can navigate the challenges of atopic dermatitis. This proactive approach not only alleviates physical discomfort but also enhances overall well-being, empowering those affected to live more comfortably with this chronic condition.